
test

Cell Tower
Basic Definition Technology Coverage & Capacity Pros & Cons Types
Broadband Types
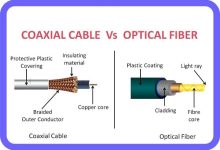
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Cable Internet Fiber Internet Satellite Internet Mobile Broadband (4G/5G) Type Technology Speed Range Pros Cons Best For DSL Telephone lines 1–100 Mbps / 1–10 Mbps Widely available, cheap Slow, distance-sensitive Rural/suburban Cable Coaxial cables 50 Mbps–1 Gbps / 5–50 Mbps Faster than DSL, common Shared bandwidth, weak upload Urban households Fiber Fiber-optic cables 1–10 Gbps+ (symmetrical) Fastest, reliable, low latency Expensive, limited coverage Heavy users/business Satellite Satellites 25–250 Mbps / 5–20 Mbps Works anywhere High latency, weather issues Remote areas Mobile Cellular (4G/5G) 10 Mbps–1 Gbps+ Portable, flexible Coverage/data caps On-the-go users
Bandwidth & Speed
Bandwidth Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given time. Usually measured in bits per second (bps), such as Mbps (megabits per second) or Gbps (gigabits per second). Key Points Speed Speed in networking refers to how quickly data travels from one point to another. It is the rate of data transfer experienced by the user, often measured in bits per second (bps), just like bandwidth. Key Points Bandwidth vs Speed vs Throughput Term Definition Example Key Point Bandwidth Maximum capacity of a network link, measured in bits per second (bps). A fiber line with 1 Gbps bandwidth Think of it as the width of the highway (how many cars...
Data Unit
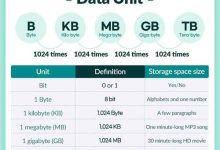
What is a Data Unit? A data unit is the basic piece of information used in computing and networking. Depending on the context, it can mean: Storage / Capacity Data Units These measure the size of data in computers and digital systems: Used to describe file sizes, disk capacity, memory, and bandwidth. Networking Transmission Data Units (OSI Model) These describe how data is packaged and transmitted across networks: Each layer adds headers/trailers to guide transmission and ensure reliable communication. Bandwidth and Data Units Final Summary
Data Center
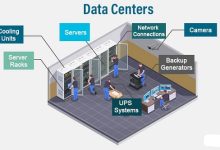
What Is a Data Center? Key Components Types of Data Centers Global Scale Why They Matter

Submarine Cables
What Are Submarine Cables? History Structure of Modern Submarine Cables A typical cross‑section includes: Deployment Global Scale

Terrestrial Fiber
What Is Terrestrial Fiber? Structure & Technology Types of Terrestrial Fiber Networks Global Scale

Satellite Links
How Satellite Links Work Types of Satellite Links Applications Comparison with Other Infrastructure Feature Submarine Cables Terrestrial Fiber Satellite Links Coverage Intercontinental National/regional Global, including remote areas Latency Very low Very low Higher (depends on orbit) Capacity Extremely high Extremely high Lower than fiber/cables Reliability High High Weather/space conditions affect Deployment Undersea cable ships Underground/land routes Launch satellites into orbit

Hosting
Hosting refers to providing space and resources on servers so that websites, applications, or services can be accessible over the internet.It allows individuals and organizations to publish content online without needing to own and manage their own physical servers. Types of Hosting 1. Shared Hosting 2. VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server) 3. Dedicated Hosting 4. Cloud Hosting 5. Managed Hosting
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on‑demand delivery of computing resources over the internet. These resources include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics. Instead of owning hardware, organizations and individuals rent resources from cloud providers, paying only for what they use. Core Principles Deployment Models Cloud Computing Products & Services 1.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) 2. Platform as a Service (PaaS) 3. Software as a Service (SaaS) 4. Container as a Service (CaaS) 5. Function as a Service (FaaS / Serverless)
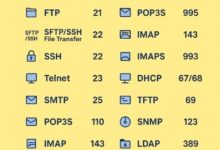
Protocols and Ports
What Are Protocols? What Are Ports? Common Protocols & Ports Protocol Port Transport Use HTTP 80 TCP Web traffic (unencrypted) HTTPS 443 TCP Secure web traffic FTP 21 TCP File transfer SMTP 25 TCP Sending email DNS 53 UDP/TCP Domain name resolution SSH 22 TCP Secure remote login Telnet 23 TCP Remote login (insecure, legacy) SNMP 161 UDP Network management NTP 123 UDP Time synchronization How Protocols & Ports Work Together Security Considerations Summary:






 Acer
Acer Apple
Apple ASUS
ASUS Dell
Dell

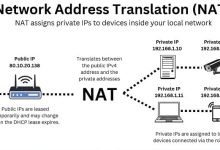


Latest Comments
666